Introduction
Technology has undergone a profound revolution with the integration of AI systems, bringing about transformative changes across all sectors and enhancing the quality of human life (Javaid et al., 2023). We are currently witnessing innovations that mark the advent of a new era in our way of life. A new era in living that embodies the distinctive experiences, cultural impacts, and technological advancements that have molded individuals, setting the stage for future generations (Islam & Islam, 2023). This uprising development has arrived and emerged an era of productivity with a period characterized by increased efficiency, output, and innovation in various sectors, driven by advancements in technology, processes, and management practices (Bahrini et al., 2023). During such eras, there is a heightened focus on optimizing resources, streamlining workflows, and achieving higher levels of output and big growth. Its exact nature and scope can vary, but it typically involves a significant boost in overall productivity and economic performance (Gill & Kaur, 2023).
This technological shift commenced with what is commonly known as ChatGPT, originating from the artificial intelligence research organization, OpenAI. ChatGPT stands as a natural language processing (NLP) model, fusing together GPT-2, a language model based on transformers that OpenAI developed, with a combination of supervised and reinforcement learning methods. These techniques were employed to fine-tune the model, drawing from the approach of transfer learning, on the GPT-3 group of extensive language patterns, also developed by OpenAI. The model facilitates seamless, natural interactions between users and an AI system via text-based conversations. Its potential applications encompass customer service solutions and the development of virtual assistants adept at engaging in both voice and text-based dialogues. ChatGPT boasts additional functionalities, including the capacity for topic identification, emotion recognition, and sentiment analysis. These features serve to enhance user comprehension and engagement with their conversational counterpart. Moreover, it possesses the capability to generate multiple conversational threads, thereby enhancing the authenticity of interactions between users and AI systems. Furthermore, our exploration will extend to the formidable challenges that confront AI development and the strategies for surmounting them (Ray, 2023).
To comprehend the magnitude of the transformation being pursued, it is imperative to delve into the progress and evolution observed in technology and innovation across diverse domains. The ongoing transformation, encompassing artificial intelligence and machine learning, holds the potential to enhance various facets of our lives. These enhancements span healthcare, transportation, sustainable energy, education, manufacturing, agriculture, commerce, communications, and numerous other fields. This transformation stands to yield significant improvements in process efficiency, time and resource savings, and the alignment of efforts toward critical priorities such as climate change mitigation and environmental sustainability. Additionally, it has the potential to reduce disparities in access to services and opportunities among different social and economic strata. Furthermore, it is paramount that we earnestly address the ethical, social, and legal challenges that may arise as a consequence of this transformation. Responsible and sustainable technology deployment, equitable access, and personal privacy safeguards are imperative considerations.
The next section involves a short literature review illustrating the answer to what is ChatGPT and a few applications of it in life sectors, while the third section establishes a discussion and analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of the utilization of ChatGPT in higher education. This is followed by the last section that concludes this study.
1. Literature Review
1.1. What is ChatGPT?
A chatbot, known as ChatGPT, is a software program developed by OpenAI based in San Francisco. It was released for free public testing on November 30, 2022. ChatGPT is an advanced chatbot that utilizes OpenAI’s GPT technology to simulate human-like conversations. It is designed to handle various types of text-based requests, from simple queries to more complex tasks. The chatbot is trained on a large amount of data, making it proficient in generating well-written and meaningful responses. It can assist users in tasks such as composing messages or addressing productivity issues with colleagues (Cao, 2023). Additionally, ChatGPT’s extensive database and efficient architecture make it useful for academic researchers, as it can even generate dissertations on topics related to artificial intelligence. The ChatGPT model is trained using a method called Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback. This technique is similar to how the InstructGPT model is trained, but with some slight differences in how the data is collected (Meyer et al., 2023). To train ChatGPT, an initial model is first trained using supervised fine-tuning. AI trainers have conversations where they play the roles of both the user and an AI assistant. They are given suggestions from the model to help them compose their responses. The conversations generated by the trainers are used to create a new dataset specifically for training ChatGPT. This dataset is combined with the Instruct GPT dataset, which is converted into a dialogue format. The reward model for reinforcement learning is built as follows: we need to collect comparison data consisting of multiple responses from different models, which are then graded based on their quality. To gather this data, we recorded conversations between AI trainers and the Chatbot. We randomly selected a phrase generated by the model and sampled different possible completions, which were then evaluated and scored by AI trainers. This scoring process was repeated multiple times to obtain a diverse set of comparison data. Finally, we can utilize a method called Proximal Policy Optimization to fine-tune the model using these reward models, improving its performance over time (Cao, 2023).
1.2. ChatGPT in Various Sectors
Since January 2022, ChatGPT and similar AI language models have been used in various domains and industries. The adoption of ChatGPT can vary based on specific needs and applications. However, some trends are apparent (Ray, 2023). Many companies have integrated AI-powered chatbots like ChatGPT to handle customer inquiries, provide instant responses, and improve customer service efficiency. Furthermore, ChatGPT has been used to generate content for blogs, news articles, and marketing materials, automating content creation tasks. Additionally, ChatGPT is used to develop educational tools, virtual tutors, and learning assistants to provide students with personalized guidance and answers to their questions.
In healthcare, ChatGPT is employed to provide information to patients, assist with appointment scheduling, and answer general medical queries. Recently, researchers and writers have used AI models like ChatGPT for assistance in generating ideas, drafting content, and conducting literature reviews. Besides, ChatGPT can help with legal research, document review, and drafting legal documents (Cao, 2023).
In finance and investment, AI models like ChatGPT are used for risk assessment, investment analysis, and portfolio management. Additionally, ChatGPT is integrated into e-commerce websites and applications to assist customers with product recommendations, answer questions, and provide support. Some companies use ChatGPT for initial candidate screening, answering HR-related queries, and automating routine HR tasks. It’s important to note that the use of AI models can expand into new domains as technology evolves, and organizations continue to explore innovative applications. The adoption of AI in each domain can vary depending on the specific needs and goals of businesses and institutions. For the most current information on AI model adoption, it’s advisable to consult industry reports, news sources, and research publications beyond my last knowledge update (Dwivedi et al., 2023).
Beyond education and research, ChatGPT’s applications extend to various industries. Its ability to provide quick and rapid responses makes it a valuable tool for customer service, support, and information retrieval (Kasneci et al., 2023). The capacity of ChatGPT to generate coherent and well-written text also makes it useful for content creation and marketing purposes (Bahrini et al., 2023). While challenges may arise with integrating ChatGPT directly for certain tasks, alternative approaches, such as generating high-quality synthetic data and fine-tuning local models, can overcome these limitations (Ray, 2023).
1.2.1. Healthcare Sector
Given that the healthcare and medicine domain is the most crucial sector, ChatGPT can be employed in various ways to improve patient care, streamline administrative processes, enhance medical research, and provide valuable information to both healthcare professionals and patients. ChatGPT can serve as a virtual health educator, providing patients with information about their medical conditions, treatment options, and post-operative care. It can answer common patient questions, offer dietary advice, and help patients better understand their health. On the other hand, it can be implemented to handle appointment scheduling, rescheduling, and cancellations. It can also send automated reminders to patients about upcoming appointments, helping reduce no-show rates. ChatGPT can assist patients in assessing their symptoms and provide recommendations on whether they should seek immediate medical attention or schedule an appointment with a healthcare provider. In terms of medication management, ChatGPT can help patients manage their medications by sending reminders, explaining dosages, and offering information on potential side effects or interactions with other drugs. Furthermore, patients can use ChatGPT to access their medical records and receive explanations of their lab results, diagnostic reports, and treatment history in a user-friendly manner. Healthcare professionals can use ChatGPT to access quick reference information, such as drug interactions, treatment guidelines, or the latest research findings, which can help in clinical decision-making. It is worth mentioning that ChatGPT can be integrated into telemedicine platforms to assist in patient interviews, gather medical histories, and provide preliminary assessments before a doctor’s consultation. Other applications of ChatGPT in medical coding and billing where it can assist medical coders and billers by generating accurate codes based on provided patient information, helping streamline the revenue cycle management process. More examples such as mental health support, public health information, epidemiological analysis, medical device troubleshooting are the most current utilization of ChatGPT (Mhlanga, 2023), (Ray, 2023).
These deployments have many advantages and disadvantages, some are cited respectively (Bahrini et al., 2023):
-
Patient Assistance: AI-powered chatbots can provide 24/7 support to answer general health questions and offer information about symptoms and medical conditions. For example, a patient can inquire about flu symptoms and receive guidance on whether they should seek medical attention.
-
Data Analysis: AI can analyze large volumes of medical data to identify trends, patterns, and potential outbreaks. This can aid in disease monitoring and management, such as tracking the spread of infectious diseases like COVID-19.
-
Remote Monitoring: AI can continuously monitor patient data, such as vital signs, and alert healthcare providers to any irregularities. For instance, wearable devices equipped with AI can monitor an elderly person’s heart rate and alert a caregiver in case of an abnormal reading.
-
Data Privacy: Handling sensitive patient data requires strict adherence to privacy regulations, such as HIPAA in the United States. Unauthorized access to healthcare information can result in privacy breaches and legal consequences.
-
Misdiagnosis: AI, including ChatGPT, may not always provide accurate medical advice or diagnosis. Relying solely on AI for critical medical decisions can lead to incorrect treatment recommendations and harm to patients.
1.2.2. Business Sector
Second most important sector is the economics domain, the popular implementations of ChatGPT in the business and finance sector are (George & George, 2023):
-
Customer Support Chatbots: Implement ChatGPT-powered chatbots on financial institution websites or apps to handle customer inquiries and provide support around the clock. These chatbots can assist with account-related queries, explain financial products, and guide users through basic transactions, reducing the workload on human customer support agents.
-
Financial Advisory Services: Integrate ChatGPT as a virtual financial advisor on financial services websites and apps. Users can interact with the chatbot to receive personalized financial advice, investment recommendations, and retirement planning strategies based on their financial goals and risk tolerance.
-
Market Analysis and Sentiment Analysis Tools: Develop ChatGPT-driven tools that analyze market data, news articles, and social media to provide real-time market insights and sentiment analysis. This can help traders and investors make informed decisions by identifying trends and assessing market sentiment.
-
Automated Trading Algorithms: Utilize ChatGPT to create and optimize automated trading algorithms. These algorithms can continuously monitor market data, execute trades, and adapt to changing market conditions, potentially optimizing investment portfolios and trading strategies.
-
Credit Scoring and Loan Approval Systems: Integrate ChatGPT into the loan approval process to assess credit risk and make lending decisions. It can analyze applicant data, such as credit history and financial information, and provide recommendations regarding loan approvals or denials. Many advantages and disadvantages can be cited:
-
Instant Responses: AI-powered chatbots can provide quick responses to customer inquiries, enhancing customer satisfaction and reducing response time. For example, an e-commerce website can use AI chatbots to help customers with product recommendations and order tracking.
-
Cost-Effective: AI can handle a large volume of customer queries simultaneously, reducing the need for a large customer service staff and ultimately saving costs.
-
Algorithmic Bias: AI models can perpetuate biases present in historical financial data, potentially leading to unfair or discriminatory financial decisions.
-
Lack of Accountability: Errors made by AI in financial decisions may lack clear accountability, making it challenging to address financial losses or regulatory violations.
-
Consistency: AI ensures that customers receive consistent and accurate information regardless of the time of day or the agent they interact with.
-
Risk Assessment: AI can analyze financial data to assess market trends and predict investment risks, helping investment professionals make more informed decisions.
-
Fraud Detection: AI can detect unusual patterns and behaviors in financial transactions, aiding in the prevention of fraudulent activities like credit card fraud and money laundering.
-
Automation: AI can automate routine financial tasks, such as portfolio management, reducing errors and saving time.
-
Lack of Empathy: AI may struggle to understand and respond effectively to emotionally charged customer issues, leading to frustration among customers seeking empathetic support.
-
Complex Queries: AI may have limitations in addressing complex or unique customer problems, requiring human intervention in certain cases.
-
Document Review: AI can quickly review and analyze legal documents, saving time for legal professionals during legal discovery and research.
-
Research Assistance: AI can assist in legal research, helping lawyers find relevant case law and precedents more efficiently.
-
Predictive Analysis: AI can help predict legal outcomes based on historical data, aiding in litigation strategy.
-
Ethical Concerns: AI may have limitations in making ethical judgments, which are crucial in the legal field, particularly in cases involving sensitive issues or subjective interpretations of the law.
-
Quality Assurance: Legal professionals must ensure that AI-generated content meets the necessary standards and accuracy required for legal documents and cases.
-
Automation: AI can control and optimize manufacturing processes, leading to increased efficiency and reduced labor costs. For example, in automotive manufacturing, robots guided by AI can assemble vehicles with precision and speed.
-
Quality Control: AI can detect defects in real-time, ensuring product quality. In semiconductor manufacturing, AI-powered vision systems can identify imperfections in microchips.
-
Predictive Maintenance: AI can predict equipment failures and maintenance needs, reducing downtime and saving costs. In the aviation industry, AI can analyze sensor data to forecast when aircraft components need maintenance.
-
Job Displacement: Automation may lead to job losses for factory workers, necessitating retraining and job transition programs.
-
Initial Investment: Implementing AI in manufacturing requires a significant upfront investment in technology and training.
In each sector, the successful integration of AI like ChatGPT depends on careful consideration of the advantages and disadvantages specific to that industry, as well as addressing potential ethical, privacy, and regulatory concerns.
1.3. ChatGPT in Higher education
In the realm of higher education, ChatGPT holds significant promise, offering a range of applications that can enhance learning and teaching experiences, administrative processes, and research endeavors. Some exclusive papers have presented the uses of ChatGPT in higher education (Kasneci et al., 2023), (Mhlanga, 2023):
1.3.1. Learning and Teaching Experiences
The first category, encompassing learning and teaching experiences, represents a transformative use of ChatGPT in the field of education. In this category, ChatGPT serves as an innovative tool designed to enhance the learning journey and teaching methodologies. By offering personalized support, interactive learning resources, and accessibility solutions, ChatGPT contributes to the evolution of educational practices and fosters a dynamic and inclusive educational environment. From acting as a virtual tutor to facilitating language learning and aiding with homework, ChatGPT’s applications in learning and teaching aim to cater to diverse learning styles and preferences, ultimately elevating the educational experience for students of all levels, including (Cao, 2023):
-
Personalized Tutoring and Learning Assistance: ChatGPT can serve as a virtual tutor, providing personalized guidance to students on a wide array of academic subjects. For instance, in a mathematics course, ChatGPT can help students solve complex equations, offer step-by-step explanations of theorems, and provide practice problems tailored to individual learning needs. This individualized approach to learning can foster deeper comprehension and improve academic performance.
-
Language Learning Support: It can facilitate language learning by engaging in conversations, providing vocabulary exercises, and offering pronunciation guidance.
-
Homework and Quiz Assistance: ChatGPT can assist students in solving homework problems, provide hints, and generate practice quizzes to help with assessment preparation.
-
Study Group Facilitation: It can encourage and organize online study groups, fostering peer-to-peer learning and collaborative discussions.
-
Accessibility Support: ChatGPT can assist students with disabilities by offering text-to-speech and speech-to-text capabilities, making learning materials more accessible.
-
Academic Advising and Career Guidance: ChatGPT can assist both teachers and students in their academic and career planning. It can provide insights into degree requirements, suggest suitable majors, recommend internship opportunities, and even offer resume-building tips. They can engage in discussions with ChatGPT to receive guidance on selecting courses aligned with their career aspirations.
-
Grading and Assignment Feedback: ChatGPT can assist educators in grading assignments and providing constructive feedback. It can automatically evaluate and grade assignments, offering explanations and suggestions to students. This helps maintain consistency in grading and offers students insights into their performance.
1.3.2. Administrative Processes
The second category, (Fuchs, 2023)involving administrative processes, introduces ChatGPT as a multifaceted administrative assistant within educational institutions. In this role, ChatGPT streamlines various administrative tasks and processes, making the management of educational activities more efficient and user-friendly (Cao, 2023). By responding to student inquiries about course information and registration, providing academic advising and career guidance, automating grading and assignment feedback, and even aiding in teacher professional development, ChatGPT simplifies the administrative complexities that often accompany education. Moreover, by offering solutions for plagiarism detection and facilitating internship matching, ChatGPT contributes to maintaining academic integrity and connecting students with valuable real-world opportunities. In essence, ChatGPT’s applications in administrative processes enhance the operational aspects of education, making the administrative side of the educational journey more streamlined and accessible (Haleem et al., 2022).
-
Course Information and Registration: Institutions can employ ChatGPT to streamline administrative tasks. Students can inquire about course schedules, prerequisites, and availability, and even complete course registration processes. For instance, students might ask the chatbot for a list of biology courses available in the upcoming semester and proceed to register for a specific course directly through the chat interface (AlAfnan et al., 2023) .
-
Teacher Professional Development: Educators can use ChatGPT to access resources, lesson plan ideas, and pedagogical insights for professional development.
-
Plagiarism Detection: Institutions can employ ChatGPT to detect and prevent academic dishonesty by analyzing student submissions for originality (Haleem et al., 2022) (Bahrini et al., 2023).
1.3.3. Research Endeavors
The third category, which revolves around research endeavors, highlights ChatGPT as a versatile tool that can significantly impact the landscape of academic and scientific research. ChatGPT’s applications in this realm extend across various stages of the research process, from literature review and data analysis to information retrieval and language translation. In this context, ChatGPT serves as a valuable research assistant, capable of summarizing scholarly articles, identifying relevant studies, and speeding up the often-time-consuming process of literature review. It aids researchers in staying up-to-date with the latest research trends and findings (Ray, 2023). Furthermore, ChatGPT offers data analysis and interpretation capabilities, helping researchers generate insights from complex datasets. This not only accelerates the research process but also aids in deriving meaningful conclusions from large volumes of data. ChatGPT’s language translation and transcription services are also pivotal, ensuring that research findings are accessible to a global audience. It can translate documents, transcribe interviews, and break down language barriers, fostering international collaboration in research. Finally, ChatGPT is capable of automating report generation, simplifying the process of producing research reports, summaries, and data visualizations. By offering these services, ChatGPT enhances the efficiency of research endeavors and supports the dissemination of research findings to a broader audience (Opara et al., 2023).
-
Literature Review: ChatGPT can assist researchers in conducting literature reviews by summarizing scholarly articles and identifying relevant studies.
-
Information Retrieval: It can retrieve information, research papers, and references related to specific research topics, speeding up the research process.
-
Data Analysis and Interpretation: ChatGPT can help researchers with data analysis, generating insights from datasets and summarizing research findings.
-
Language Translation and Transcription: Researchers can use ChatGPT for translation tasks, transcribing interviews, and translating documents into various languages.
-
Automated Report Generation: ChatGPT can assist in generating research reports, research summaries, and data visualizations for research publications.
These applications of ChatGPT demonstrate its versatility and utility across the spectrum of learning and teaching, administrative tasks, and research efforts in the educational sector. Their advantages and disadvantages are numerous (see Table 1):
-
Personalized Learning: AI can adapt educational content to individual students’ learning styles and abilities. For example, adaptive learning platforms can tailor lessons to suit a student’s strengths and weaknesses.
-
24/7 Support: AI tutors and virtual assistants can be available around the clock to answer student questions, offer explanations, and provide additional resources for learning.
-
Automated Grading: AI can automate the grading of assignments and tests, providing students with prompt feedback and allowing educators to focus on teaching.
-
Loss of Human Interaction: Excessive reliance on AI can reduce the importance of human educators and peer interaction in the learning process, potentially impacting the social and emotional development of students.
-
-
Quality Control: Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of educational content generated by AI can be challenging, and errors in content may go undetected.
-
Bias and Fairness: AI models can inherit biases from the data they are trained on, which can lead to biased or unfair outputs. For example, ChatGPT may generate responses that reflect societal biases or exhibit discrimination. Addressing and mitigating bias in AI models is an ongoing challenge (Xames & Shefa, 2023).
-
Lack of Common Sense: AI models like ChatGPT may lack common sense reasoning and may produce plausible-sounding but incorrect or nonsensical answers to questions. This limitation can affect the quality of responses.
-
Context Sensitivity: AI models may struggle with understanding and maintaining context over long conversations. They can lose track of the conversation topic or provide responses that don’t align with the context of the discussion.
-
Safety and Ethical Concerns: There are concerns about the potential for AI models to be used for malicious purposes, including spreading misinformation, deepfakes, and other forms of harmful content. Ensuring the ethical use of AI models is a significant challenge.
-
Data Privacy and Security: The use of AI models, especially in applications that involve personal data, raises concerns about data privacy and security. Ensuring that sensitive information is handled appropriately is critical.
-
Scalability and Efficiency: Some AI models, including ChatGPT, can be computationally intensive and resource-hungry. Optimizing these models for efficiency and scaling them to handle high volumes of requests is a technical challenge.
-
Training Data and Domain Specificity: AI models are often trained on a diverse range of data, which can limit their ability to provide specialized or domain-specific knowledge. Fine-tuning and customization may be needed to make them more useful in specific contexts.
-
OpenAI’s Model Policies: Users and developers of AI models must adhere to the policies and guidelines set by organizations like OpenAI to ensure responsible and ethical usage. Staying compliant with these policies can be a technical challenge.
-
Algorithmic Improvements: Continual research and development are required to improve AI models like ChatGPT. Enhancing their capabilities and addressing limitations is an ongoing technical endeavor.
-
Interoperability: Integrating AI models into various applications and platforms may require technical adaptations and ensuring compatibility with existing software and systems.
-
Evaluation and Metrics: Developing robust evaluation metrics for AI models, especially those focused on natural language understanding and generation, is a technical challenge. It’s essential to measure their performance accurately.
-
Hardware and Infrastructure: Running large AI models efficiently often requires specialized hardware and infrastructure. Optimizing these aspects for scalability and performance is a technical concern.
-
To address these technical issues, researchers and developers in the AI community continually work to improve AI models, develop better training data, and create guidelines for responsible AI use. Collaboration between organizations, researchers, and the broader AI community is essential to make AI models more reliable, ethical, and beneficial (Adeshola & Adepoju, 2023; AlAfnan et al., 2023; Islam & Islam, 2023; Javaid et al., 2023; Kasneci et al., 2023).
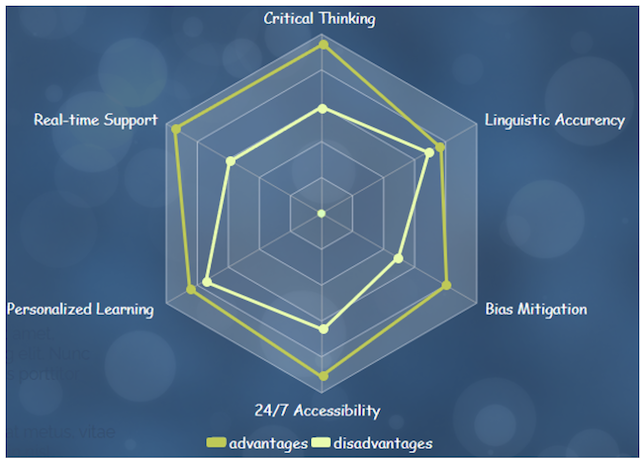
The radar chart (Figure 1) provides a visual representation of the perceived strengths and weaknesses of using ChatGPT in education across various dimensions.
-
Critical Thinking (Advantages : 85 %, Disadvantages : 60 %) :
-
Advantages: ChatGPT excels in promoting critical thinking by generating diverse responses and encouraging exploration of different perspectives.
-
Disadvantages: There might be limitations in truly understanding nuanced or complex concepts, leading to potential gaps in fostering deep critical thinking.
-
Linguistic Accuracy (Advantages : 75 %, Disadvantages : 70 %) :
-
Advantages: ChatGPT demonstrates a high level of linguistic accuracy, offering well-constructed and grammatically sound responses.
-
Disadvantages: Despite its proficiency, occasional inaccuracies may arise, impacting the reliability of conveyed information.
-
Bias Mitigation (Advantages : 80 %, Disadvantages : 50 %) :
-
Advantages: Efforts in bias mitigation make ChatGPT a valuable tool for promoting fair and unbiased content in educational interactions.
-
Disadvantages: Despite improvements, there is still room for addressing potential biases in responses, posing challenges in ensuring complete neutrality.
-
24/7 Accessibility (Advantages : 90 %, Disadvantages : 65 %) :
-
Advantages: ChatGPT’s availability around the clock facilitates constant access to learning resources, fostering flexibility in educational engagement.
-
Disadvantages: Challenges such as potential server downtime or technical issues may hinder seamless 24/7 accessibility.
-
Personalized Learning (Advantages : 85 %, Disadvantages : 75 %) :
-
Advantages: ChatGPT excels in delivering personalized learning experiences by tailoring responses to individual needs and learning styles.
-
Disadvantages: The challenge lies in fully understanding the unique requirements of each learner, potentially leading to inaccuracies in personalization.
-
Real-time On-demand Support (Advantages: 95%, Disadvantages: 60%):
-
Advantages: ChatGPT’s ability to provide real-time on-demand support enhances the learning experience by offering immediate assistance and clarification.
-
Disadvantages: While highly responsive, there may be instances where the model struggles to address complex queries promptly, affecting the real-time support experience.
It’s important to note that these percentages are subjective and based on general perceptions. The effectiveness of ChatGPT in education can vary depending on specific use cases, implementation strategies, and individual preferences.
Figure N° 1. The radar chart of using ChatGPT in education across various dimensions
Table 1. Summary of advantages and disadvantages of Using ChatGPT in Higher Education
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
|
Student |
Personalized Learning |
Accuracy Concerns |
|
On-Demand Support |
Over-Reliance on Technology |
|
|
Flexibility and Accessibility |
Bias and Inequality |
|
|
Diverse Learning Formats |
Linguistic Limitations |
|
|
Efficiency in Routine Tasks |
Loss of Human Touch |
|
|
Scalability |
Challenges in Complex Interactions |
|
|
Real-time Feedback |
Privacy Concerns |
|
|
Access to Vast Information Resources |
Potential for Misinformation |
|
|
Enhanced Learning |
Cheating Concerns |
|
|
Educators |
Time Efficiency |
Loss of Personal Connection |
|
Personalized Feedback |
Quality Assurance Challenges |
|
|
On-Demand Support |
Over-Reliance on Technology |
|
|
Enhanced Teaching Resources |
Adaptability to Varied Learning Styles |
|
|
Automated Grading and Assessment |
Dependence on Pre-existing Data Quality |
|
|
Advanced Monitoring |
Detection Challenges |
|
|
Institutions Administrators |
Resource Optimization |
Ethical Considerations |
|
Innovative Support Services |
Implementation Costs |
|
|
Data-Driven Decision Making |
Technical Challenges in Implementation |
|
|
Improved Institutional Efficiency |
Maintenance Complexity |
|
|
Promoting Ethical Use |
Unintentional Misuse |
|
|
Policy Implementation |
Policy Enforcement |
|
|
Maintaining Integrity |
Potential Threat |
2. Discussion and Analysis
The integration of ChatGPT into higher education offers a spectrum of advantages and disadvantages. Students stand to gain from personalized learning experiences tailored to their individual needs, on-demand support providing instant assistance, and enhanced flexibility with diverse learning formats. Efficiency in routine tasks, scalability, and real-time feedback contribute to an enriched learning environment. Access to vast information resources and the potential for enhanced learning through various formats further enrich the educational experience. Educators benefit from time efficiency through automated grading and assessment, personalized feedback mechanisms, and access to a wealth of teaching resources that cater to varied learning styles. Advanced monitoring tools also assist in tracking student progress (George & George, 2023; Whalen & Mouza, 2023).
However, these advantages are accompanied by notable concerns. The potential for inaccuracies in the information delivered raises questions about the reliability of ChatGPT-generated content. Issues of bias and inequality must be addressed to ensure equitable access to education. Over-reliance on technology poses a risk of diminishing the human touch in education, impacting the overall learning experience. Challenges in handling complex interactions and ensuring the quality of educational engagement may arise as institutions scale their use of ChatGPT (AlAfnan et al., 2023).
For educators, the risk of a diminished personal connection with students due to increased reliance on technology calls for a careful balance between efficiency and maintaining the human element in education. Ensuring the quality assurance of personalized feedback becomes a challenge that requires ongoing attention. The dependence on pre-existing data quality for teaching resources raises concerns about the relevance and accuracy of the educational material provided (Bahrini et al., 2023; Cao, 2023).
Institutional administrators benefit from resource optimization and improved efficiency through data-driven decision-making. Yet, ethical considerations related to the implementation of innovative support services, including concerns about privacy and unintentional misuse, necessitate careful policy implementation and enforcement. Implementation costs and technical challenges associated with integrating ChatGPT into existing systems further complicate the landscape. The need for ongoing maintenance and updates introduces complexity into the otherwise streamlined efficiencies ChatGPT promises (Javaid et al., 2023).
In summary, the integration of ChatGPT into higher education offers a myriad of benefits, but careful attention must be paid to the associated challenges. Striking a balance between leveraging technology for efficiency and maintaining the integrity and personalization of the educational experience is key. As stakeholders navigate this transformative shift, robust policies, ongoing research, and collaborative efforts are essential to maximize the advantages of ChatGPT while mitigating potential drawbacks and ensuring responsible and ethical use in the evolving landscape of higher education.
Conclusion
In the expansive realm of literature exploring the integration of ChatGPT across diverse life sectors, this thorough review highlights the transformative potential of this language model. As ChatGPT permeates various domains, its application in higher education emerges with a tapestry of advantages and nuanced challenges. The merits, ranging from personalized learning and on-demand support to institutional efficiencies and data-driven decision-making, promise a paradigm shift in educational approaches. Yet, a discerning analysis unravels the intricacies of potential inaccuracies, biases, and privacy concerns, prompting a reflection on whether ChatGPT represents a boon or a potential threat to higher education. On one hand, the advantages underscore the potential for revolutionizing the educational landscape, fostering tailored learning experiences and bolstering institutional efficacy. However, the shadows of concerns loom large – the risk of an over-reliance on technology, the potential for biases impacting educational equity, and the imperative of preserving the human touch in education. This duality prompts a nuanced examination, inviting readers to consider whether ChatGPT, as an innovation, is a catalyst for positive change or introduces challenges that may undermine the fundamental values of higher education. Navigating this dynamic landscape demands not only a thorough understanding of the technological intricacies but also a careful consideration of the ethical and pedagogical implications. Stakeholders are challenged to engage in ongoing research, develop robust policies, and foster collaborative efforts to harness the full potential of ChatGPT, ensuring that its integration into higher education aligns with the overarching goal of enhancing the educational experience without compromising its core principles. As we look towards the future, recommendations include the establishment of interdisciplinary research initiatives that bring together experts in artificial intelligence, education, and ethics to continuously monitor and assess the impact of ChatGPT. The development of clear guidelines and standards for the ethical use of AI in education should be prioritized, fostering responsible practices and mitigating potential risks. Additionally, institutions should invest in professional development programs to equip educators with the skills needed to navigate the evolving landscape of AI-driven education. Future research endeavors should focus on refining the algorithms powering ChatGPT to address issues of bias and accuracy, exploring ways to enhance the model’s adaptability to diverse learning styles. Moreover, investigating the long-term effects of ChatGPT integration on student engagement, academic performance, and the overall quality of education will provide valuable insights. By embracing a collaborative and forward-thinking approach, the educational community can unlock the full potential of ChatGPT while proactively addressing emerging challenges.