With the spread and development of English around the world, English is used as a foreign language in a country like Algeria (together with French as a first foreign language). As the number of English learners is increasing, different teaching methods have been implemented to test the effectiveness of the teaching process. The new era assigns new challenges and duties on the modern teacher. The tradition of English teaching has been drastically changed with the remarkable entry of technology. Technology provides so many options as making teaching interesting and also making teaching more productive in terms of improvements. It is utilized to satisfy both visual and auditory senses of the students. With the spread and development of English around the world, English has been learned and used by more and more speakers.
The influence of visual technology in teaching has proved to be undeniable in recent years. Hence, this study aimed to determine the effect of teaching first year secondary school students using power point presentations instead of relying only on textbooks and whiteboards. This article is devoted to check the effective of teaching secondary school students with power point presentations as a motivational method or technique to raise interest and involvement inside the classroom and during English sessions, in addition to the improvement of their scores and achievements in English.
Literature Review
Power point presentations
In recent years, the use of PowerPoint in the classrooms has increased significantly, and has attracted many researchers to test its effect in education. Some of the studies have tried to measure the effect of PowerPoint on the students’ attitudes and behaviors, while others have focused on its effect on the students’ academic performance. Microsoft Power-Point is a presentation program developed by Microsoft. It is a part of the Microsoft Office system which is widely used by business people, educators, students, and trainers. As a part of the Microsoft Office suite, Power-Point has become the world’s most widely used presentation program.
Supporters of Power Point Presentations like Antherson (2003), contended that cognitive achievement depends on several factors among which are the instructional methods, learning environment and the learner. The brain does not pay attention to boring things. What makes PowerPoint presentations so effective is that they add complementary, multisensory events designed to spark an emotional response among audience members. This helps maintain audience attention and improves cognitive achievement. The most effective presentations are the ones that are informative, educational, and entertaining. For instance, Gier and Kreiner (2009) who studied the effectiveness of PowerPoint in a psychology class concluded that when students were actively engaged in the class using PowerPoint presentation, information retention increased.
Cashman and Shelly (2000) find that learners learn most effectively when their five senses are involved. The PowerPoint presentations appeal to learners’ diverse learning styles, such as visual, auditory, kinesthetic, and creative by employing multimedia methods, such as sounds, images, color, action, design, and so on.
Retention
Instead of memorizing facts for a test, teachers want their students to retain the information longer than a week. Teachers find it difficult to teach more and more curriculum (Wolfe, 2001). Just covering the entire curriculum does not build strong connections in student’s memory. As students collect new information that is unfamiliar and relate that material to information they already know, then they will be able to retain this new information more easily. Students need to watch what they learn in order to remember.
Nowadays, the stereotyped traditional teaching methods and environment are unpopular, while multimedia technology featuring audio, visual animation effects naturally and humanely. Multimedia technology offers a sense of reality and functions very well, which greatly cultivates students’ interest and motivation in study and their involvement in class activities. This generation of learners is grown up in new area where technology dominates their life. They are motivated and stimulated by new technologies. For this reason they may retain more information if technology is used in their classrooms. Computers, projectors, videos, songs, audiovisuals and other technological tools are more effective strategies than the traditional methods (Miller, 2009). They spur interest in learners and are likely to motivate them to perform at a higher level.
Motivation and Technology in Education
The literature review points out that there are several contributing factors to the practicalities of a true innovation. The first contributing factor is motivation. According to Harmer (2001) “motivation is some kind of internal drive which pushes someone to do things in order to achieve something.” (p. 51). Motivation includes all of the wants, wishes, efforts, abilities, potentials, engagements, and the persistence to attain and reach desired goals in a form of positive achievement.
It also suggests that educational technology can help to motivate learners of English as a Second Language develop language skills and as stated by Eggen and Kauchak (2004 : 414), “in terms of research as having positive effects of technology on motivation in at least four areas : self-esteem and self-efficacy, attendance, attitudes, and involvement”. However, not all lecturers in schools are putting this knowledge into practice as they are still not utilizing the technology tools provided for them to use in their teaching methods. Students are becoming more advanced in the use of technology, and if teachers do not follow this trend, they will be out-of-date. In order to keep-up with the trends in education, teachers need to incorporate technology into their teaching. However, many teachers are still unaware of the benefits or purposely ignoring the fact that students enjoy using technology to learn.
When we talk about technology in education we should first define the word ICT (Information and Communication Technology). According to Kennewell (2004), ICT covers all aspects of computers, networks (including the Internet) and certain other devices with information storage and processing capacity such as calculators, mobile phones and automatic control devices and applications.
Fisher (2003) suggests using Power Point for ESL teaching. Power Point is a type of presentation software that allows users to show coloured text and images with simple animation and sound. He explains that “Power Point has been in existence for many years, it has just begun to spread to schools and ESL classrooms… [and]…the reason for this delay is that technology requires hardware, which is relatively expensive.” However, this is not a problem for presentation software like Microsoft Power Point. It is easily available and usually comes bundled with most of the office computers as part of the Microsoft Office package. Though, many are still unaware of how useful it can be as an aid in teaching. This study involves the use of Microsoft Power Point to teach and learn the English language. Effects on students’ motivation, attitude and anxiety in learning through the use of Microsoft Power Point are investigated. This provides an insight into the effectiveness of the technique with goals of improving instruction, teaching methods and other pedagogical practices employed by teachers.
Teaching English or any other foreign language in the secondary schools with large classes (35-50 students) can be said to be a nightmare for both teachers and students. As I started teaching, I found the use of power point presentations a useful audio-visual aid in my classes, especially at the beginning of each new unit where I need to introduce new notions, ideas and terminologies. At the beginning it seems to be difficult and a challenging task especially that I was not very good at using all the computer softwares. But through practice it becomes easier and enjoyable. I was astonished and amazed with the results ; students were active and involved and more concentrated during the lesson. This first experience was on 2014, where I started to integrate technology to my classrooms and to my lessons. As a result, pupils need to be involved and integrated using new methods and techniques, and we believe that Power Point Presentations are effective.
Problems with Power Point Presentation
One of the major shortcomings of using Power Point Presentations is that it relies totally on projectors which can be quite expensive to get. The second point here is that, it may happen that the projector stop suddenly or something goes wrong with it. In this case, we should never depend only on the projector. The solution is always to carry a back-up in a non-presentation form so as to replace the PPP in case something happens. Tufte (2003) thinks that the learners feel ignored in the classroom when the instructor is focusing on the presentation and not paying attention to the class, Instead of interacting with learners during the class. However, this should not prevent us from appreciating one of its useful functions. One of these is “the way it can help us crystallize our thoughts and then to arrange them” (into slides). (Rank & Warren, 2011).
Methodology
This research is done under the umbrella of the quasi experiment method using, non-randomized, non-equivalent pre-test, post-test experimental design that includes two groups. The literature in methodology highlights the importance of multiplying data sources using different types of instruments in order to diversify information sources and analyze the problem from different angles.
The Setting
The setting where teachers perform their work plays an important role in both teaching process and motivating students. In our case, our setting is Oued Taga (Brothers Yalouz) secondary school (Wilaya of Batna). The researcher deals with both teachers of English and first year scientific stream students as the sample population for the academic year 2016/2017.
Aims of the Study
This study aims also at the following objective :
-
To highlight the importance and effectiveness of power point presentations in teaching English.
To explain how technologies can be used to motivate and stimulate pupils to learn English. -
To expose teachers and students to the need of implementing new technologies in education.
-
To encourage secondary school teachers of English to use PPPs in the future life during their sessions.
Research Questions and Hypotheses
This study aims at answering the following questions :
-
What are the effects of teachers’ using PowerPoint Presentations in the class on students’ learning and scores at Oued Taga Secondary School ?
-
Can PowerPoint Presentations enhance motivation in first year secondary school students ?
Our hypothesis is derived directly from the above questions that :
-
If secondary school teachers of English make use of technologies in their classes especially power point presentations in teaching of English, then their students would get good results and they would understand better their lessons.
-
In other words, if first year (Scientific Stream) secondary school pupils are taught English using power point presentations, then they would be motivated and eager to understand more what they study.
The Participants
This was conducted with first year secondary school students in Oued Taga in Batna. Two classes from scientific stream are chosen for this investigation from a population of 210 first year students. Each class contains 35 students. This table will explain students’ number and gender
|
Gender |
Males |
Females |
|
Group 1 |
18 |
17 |
|
Group 2 |
8 |
27 |
|
Total |
26 |
44 |
Table1. information about students gender.
Research Instruments
Our present study uses the following means :
The First, Mid and Last Term Examinations
These are the usual achievement examinations taken by all the students, and they are elaborated by all the teachers of the English language in the secondary school. These examinations or tests are used to check the students’ achievements in the English language after each trimester. And the three different scores are used students’ improvement through the whole school year.
Lesson Plan
“All good teachers have some type of plan when they walk into their classrooms.”(Jensen, 2001 : 403) These lesson plans are used as maps that the teacher uses to know “what to teach, in what order, and for how much time [needed to be taught].” (Jensen, 2001 : 403) Based on these ideas the researcher designs a range of lesson plans that are used to investigate the pupils’ academic achievement and attitudes toward learning English as a foreign language. The lesson plans used in our study are designed based on the first year secondary school textbook “At the crossroads.” The researcher selected the teaching activities that fit the learners’ needs and the technology we used, and many times she rejected some of the textbook activities and replaced them by others adapted from different resources.
Questionnaires
Questionnaires are administered to both teachers of English in the secondary school and first year students to investigate students’ motivation toward learning English as a foreign language, and teachers’ opinions about using power point presentations instead of the traditional way of teaching. Teachers’ questionnaire consists of 19 questions varying from personal information to teaching methods and techniques. Students’ questionnaire is composed of 15 questions that include their opinions about the English session, the English teacher and the way they learn English.
The Treatment (The Procedure)
Each group is instructed by the researcher (their teacher), separately. Since we are working under the quasi experimental design both groups will benefit from the treatment. The sample is exposed to power-point presentations of the topics suggested in their textbook with some modifications. At the beginning of the year, a pretest is given to both groups and at the end of the year a posttest is given in order to compare the mean scores of the two groups. During the year, the same materials/lessons are taught to both groups. Each group has a total of 60 hours of power point presentations teaching within 20 weeks ; i.e. 3hrs of English learning per week for scientific stream.
The Results
The scores of students’ pretest and posttest are computed through the Statistical Package for Social Sciences SPSS 24, a paired sample t-test (p. 05) is used to calculate the students’ marks gathered from the pre/post-tests given to both the experimental and control groups.
First, the t-test is applied to verify whether or not there is a significant difference between the mean scores of the student scores in the two groups before instruction through their scores of the pre-test. As showed in table2 :
Table 2 : T-test results of the pre-test scores of the two groups in the Readiness Test.
Paired Samples Test
|
Mean |
N |
Std. Deviation |
Std. Error Mean |
T |
Sig. (1- tailled) |
|
|
Group 1 |
9,37 |
35 |
4,312 |
,729 |
-.541 |
.592 |
|
Group 2 |
9,86 |
35 |
3,291 |
,556 |
The results from the table above, shows that there is a little significant difference between the two groups in their pre-tests scores. This means that both of the groups are nearly in the same level before the treatment.
Second, the post-test scores of the two groups are also calculated and compared using t-test. The results are in the following table3 :
Table3 : t-test results of the post test scores of the two groups after treatment
Paired Samples Test
|
Mean |
N |
Std. Deviation |
Std. Error Mean |
T |
Sig. (1-tailled) |
||
|
Pair 1 |
post-test1 |
11,46 |
35 |
4,168 |
,705 |
-.967 |
.340 |
|
post-test2 |
12,29 |
35 |
3,168 |
,535 |
As table 3 presents, there is a significant difference between students’ pre-test and post-test results. The mean scores of the post-test of group1 (X1 = 11.46) is higher than the mean scores of the pre-test of the same group (X1 =9.37), and the mean scores of the post test of group 2 ( X2 =12.29) is higher than the mean scores of the same group (X2 = 9.86).
The following table explains the results of the pre and post-tests for group 1 :
Table 4 t-test results of the pre-test and post-tests of the first group.
Paired T- Test for the first group
|
Mean |
N |
Std. Deviation |
Std. Error Mean |
t |
Sig. (1 tailled) |
||
|
Pair 1 |
pre-test1 |
9,37 |
35 |
4,312 |
,729 |
-5.747 |
.000 |
|
post-test1 |
11,46 |
35 |
4,168 |
,705 |
Table 4 shows that the mean scores of the post-test has improved from ( 9.37 to 11.46) which means that there is a significant difference between pre-test scores and post-test scores. That is the treatment is somehow effective for students.
Table 5. t-test results of the pre-test and post-tests of the second group.
Paired T-Test for the second group
|
Mean |
N |
Std. Deviation |
Std. Error Mean |
t |
Sig. (1-tailled) |
||
|
Pair 1 |
pre-test2 |
9,86 |
35 |
3,291 |
,556 |
-8.525 |
.000 |
|
post-test2 |
12,29 |
35 |
3,168 |
,535 |
Table 5 represents the scores of the paired t-test of the second group in pre/post-tests. The results show a significant difference in the mean scores which means there is an improvement in the students’ scores after treatment.
The Questionnaire Results
Teachers’ questionnaire
The population of our study is the teachers of English in Oued Taga secondary schools. There are 9 teachers of English (7 females, 2 males). The number of female teachers is higher than the male one as shown in the following table:
Table 6. The Teachers’ Gender
|
Frequency |
Percent |
||
|
Gender |
male |
2 |
22,2 |
|
female |
7 |
77,8 |
|
|
Total |
9 |
100,0 |
|
Concerning the teaching experience, the majority (4 teachers) have less than 5 years experience (44.4 %), and 3 have an experience between 5 and 10 years, this reveals that most of them are novice teachers, that they have the will to use multi- techniques and tools to motivate their learners to learn English. This table explains the different teaching experience teachers had :
Table7. Teaching Experience
|
Teaching exoerience |
|||
|
less than5 years |
4 |
44,4 |
|
|
5-10years |
3 |
33,3 |
|
|
10-15 years |
1 |
11,1 |
|
|
more than 15 years |
1 |
11,1 |
|
|
Total |
9 |
100,0 |
The following table illustrates the results of teachers’ responses when asked about their students’ motivation. The results show that first year students lack motivation to learn English.
Table 8. Students’ Motivation
|
Frequency |
Percent |
||
|
Students’ Motivation |
not very |
5 |
55,6 |
|
a little |
4 |
44,4 |
|
|
Total |
9 |
100,0 |
|
When teachers are asked about their use of power point presentation to teach English in their classes, (33 %) answered sometimes, (44 %) said rarely and (22 %) said never. This reveals that they are not familiar with this technology, and most of the time they do not employed it.
Table 9. The frequency Use of PPPs
|
Frequency |
Percent |
||
|
The Use of PPPs |
never |
2 |
22,2 |
|
rarely |
4 |
44,4 |
|
|
sometimes |
3 |
33,3 |
|
|
Total |
9 |
100,0 |
Another question is asked to the teachers about their students’ reaction towards learning via power point presentations. The results show that learners like this technique and their justifications vary from one another. Some said that it attracts their attention ; others said it helped them understanding better the lessons. But all of them agreed that power point presentations
Table 10. Students’ Reaction to The Use PPPs
|
Frequency |
Percent |
||
|
Students’ Reaction To PPPs |
very much |
4 |
44,4 |
|
somehow |
3 |
33,3 |
|
|
not much |
1 |
11,1 |
|
|
Total |
8 |
88,9 |
At the end we asked them if technological tools are available in their secondary school and the majority replied by yes. As showed in the following table
Table 11. Avalability of Technology
|
Frequency |
Percent |
||
|
Availability of technology |
no |
2 |
22,2 |
|
yes |
7 |
77,8 |
|
|
Total |
9 |
100,0 |
Students’ Questionnaire
The population of the study is composed of first year secondary school scientific stream students. Our sample is 70 students (26 males and 44 females), they are aged between 15-17years old. They have learned English for four years in the middle school. The questionnaire is given to them in the English sessions with their teacher of English present there for explanation and clarifications. The questionnaires are collected after the sessions.
The following table illustrates the participants’ opinions about learning English : Figure1. Students’ opinions about Learning English
Then, they are asked about their teachers of English help in the classroom, they are asked to choose among the three options suggested.
Table 12. Characteristics of Teachers of English
|
Frequency |
Percent |
||
|
Characteristics of teachers of English |
very helpful |
48 |
68,6 |
|
helpful |
21 |
30,0 |
|
|
less helpful |
1 |
1,4 |
|
|
Total |
70 |
100,0 |
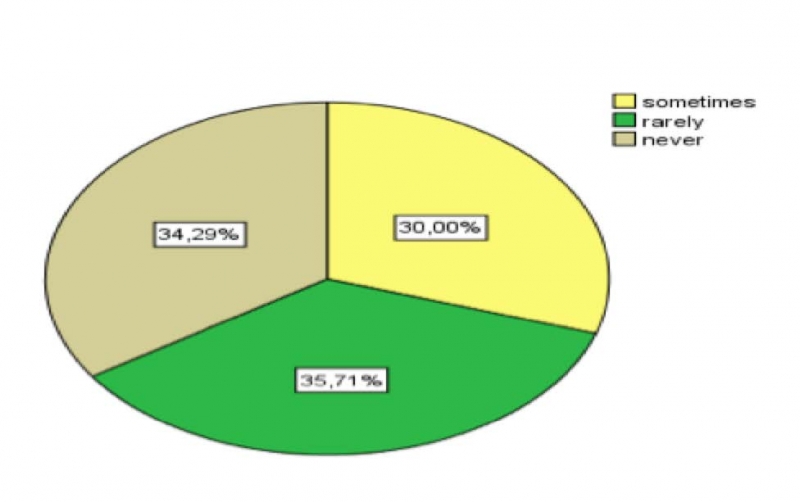
The main interest of our study is to check the use of power point presentations as a motivational tool to enhance the learning of English in secondary schools. When students asked about their teachers’ use of PPPs, the responses varied from sometimes to rarely and never. As a result, the majority of students are not exposed to this technique. The following figure summarizes their choices :
Figure2. The Use of PPPs
For the ones who answered that they are taught using this technology, another question is given about their opinions of learning via this technique, and the majority responded with a yes ( they did like it). Here are the answers :
Table13. Students’ opinion about learning with PPPs.
|
Frequency |
Percent |
||
|
Liking This technique |
no |
1 |
1,4 |
|
yes |
24 |
34,3 |
|
|
Total |
25 |
35,7 |
The last question given to students is about their opinions about learning English with the traditional way (textbooks and whiteboards) and the innovative way (power point presentations). The answers varied from yes, no, to the same , but the majority answered the same ( 42.9 %) as shown in the following table :
Table 14. The difference Between the old and new methods of learning
|
Frequency |
Percent |
||
|
The Difference between the old and new |
no |
18 |
25,7 |
|
yes |
15 |
21,4 |
|
|
methods of learning |
the same |
30 |
42,9 |
|
Total |
63 |
90,0 |
|
|
Missing |
System |
7 |
10,0 |
|
Total |
70 |
100,0 |
|
Conclusion
The main focus of our study is the implementation of power point presentation in teaching English as a foreign language in Algerian secondary schools. The null hypothesis set at the very beginning of the research is that ‘there is no significant difference between the students’ scores and motivation through learning English by the traditional method or the innovative one. The study results show that technology plays a big role in language classes ; it can be used as a tool to facilitate teaching and learning. As one of the most important goals of using new ways of teaching language in secondary schools is to promote students’ motivation towards learning, we can see in this study that using power point presentations operates as a powerful pedagogical tool in English classes. So according to the obtained results, of the post-test for the two groups has shown an improvement in students’ scores and achievements during the school year, and the continuous evaluation of learners approved that. Thus, we reject the null hypothesis.
Based on the findings of the present study and according to Radanov (2011), using PowerPoint software has several benefits for students. Its objective is acquisition of language in a funny and interactive way. It offers multimedia possibilities like sounds, images, colour, action, design, i.e., different learning styles : visual, auditory, kinaesthetic, creative, which, at the same time, means that it is attractive to various learning types. The results of the study, further, reveal that those who have learned through PowerPoint software have better values in terms of the mean in the post-test in comparison with those of the pre-test. It indicates that in using PowerPoint, learners have an intensive mental processing. As a concluding remark, we can say that power point presentations help teachers to draw students’ attention during the lesson, which increases the effectiveness of learning process.
Pedagogical Implications and Recommendations
Educational technology is playing an important role in the teaching profession but it does not mean that teachers should be totally dependent to the ICT tools. They can use Microsoft PowerPoint as a tool, not as a method. They can incorporate the use of technology to teach as a way to add variety into classroom procedures so students do not get bored. It could be a form of motivation for the students and for the teachers themselves. This study can be replicated with more participants to understand the power point presentation usage from a broader perspective. It is recommended for future researchers to investigate how to train secondary school teachers to use and implement power point presentations in their courses.
Adopting a Motivating Classroom Atmosphere
Effective teachers strive to create a motivating classroom environment. According to Wiley et al. (2003), there are two types of environments ; the physical and the psychological one ; teachers need to consider both to promote engagement and learning. The Physical Environment ; involves building a comfortable and inviting place for learning, with many educational materials readily accessible for students. For example, in dealing with pronunciation, charts and diagrams, videos, tape recorders and the use of laboratories can support the teaching/ learning process. Additionally, variation in choosing the activities may, in all probabilities, enhance learners’ improvement and prepare them to be self-regulated in the future. For instance, introducing new topics in classroom discussion, changing the shape of the classroom (U-shape), and encourage students be creative. As far as the Psychological Environment is concerned, it is based on the assumption that teachers need to promote community in their classroom, i.e., the teacher establishes frequent connections to students, motivating, supporting and encouraging them (creating a bridge between them).
Finally, the traditional method of teaching can still be the preferred instructional method by students, but teachers should pay more attention to the amelioration of this method rather than adapting a new technique by making it more interesting and live. But, an intelligent use of Power Point Presentations in teaching and learning is very important in increasing students’ achievements.